Explain How Acid-base Strength Is Different From Concentration
A proton acceptor that does not ionize fully in an aqueous solution. Acid B acid C acid A.

Strength Of Acids And Bases How To Find It Chemistry Teachoo
For bases the concentration of OH or OH is greater than 1010 7 M.
. Concentration refers to the number of moles per volume are contained within the solution. The strength of an acid or base refers to how much of the acid or bases ions are released in a solution. Acid with values less than one are considered weak.
While the concentration of the strong acid at equilibrium is zero and the concentration of the conjugate. Up to 24 cash back I am talking about the strength and concentration of acids and bases. Table of Acid and Base Strength.
Strong acids are listed at the top left hand corner of the table and have Ka values 1 2. On molecular level some of the acid will still be present as the acid partially ionizes The concentration of the weak acid at equilibrium is higher than the concentration of the conjugate base and H3O. A concentrated acid may or may not have a high acid strength.
A strong acid does not contain the maximum amount of solutes per unit volume. As a result weak acid and base solutions contain a dynamic equilibrium of several charged and uncharged species. Acid Base Solutions - Concentration and Strength.
AcidBase Strengths and Dissociation Constants. That means it depends on the concentration of H plus ions. Like weak acids weak bases can be used to make buffer solutions.
Factors Affecting AcidBase Strength. This increases the concentration of H ions in the solution. For acids the concentration of H or H is greater than 1010 7 M.
BProvide or use representations of. An acid or base which strongly conducts electricity contains a large number of ions and is called a strong acid or base and an acid or base which conducts electricity only weakly contains only a few ions and is called a weak acid or base. Up to 24 cash back Strength.
The hydrogen ion concentration decreases by a factor of 10 so the pH increases by 1 from 16 to 26. This means that if a solution has higher molarity than its concentration is higher as well. Students will be able to aGenerate or interpret molecular representations words andor pictures for acid or base solutions.
Watch for updated clicker question images. PKb 1310. 32 10 9.
Titration is a technique used in analytical chemistry to determine the concentration of an unknown acid or base. Weak acids and bases on the other hand only partially ionize and the ionization reaction is reversible. A base dissociation constant K b mathematically represents the bases relative strength and is analogous to the acid dissociation constant.
Acid A has the highest percent of ionisation given the same initial concentration of each acid because it is the strongest acid. Question A solution of hydrochloric acid with a concentration of 2 gdm 3 has a pH of 13. In organic chemistry acid-base reactions are ubiquitous.
Aqueous HCl is an example of acidic solution. Conductivity Behavior of Acids and Bases. A strong acid always has a higher acid strength.
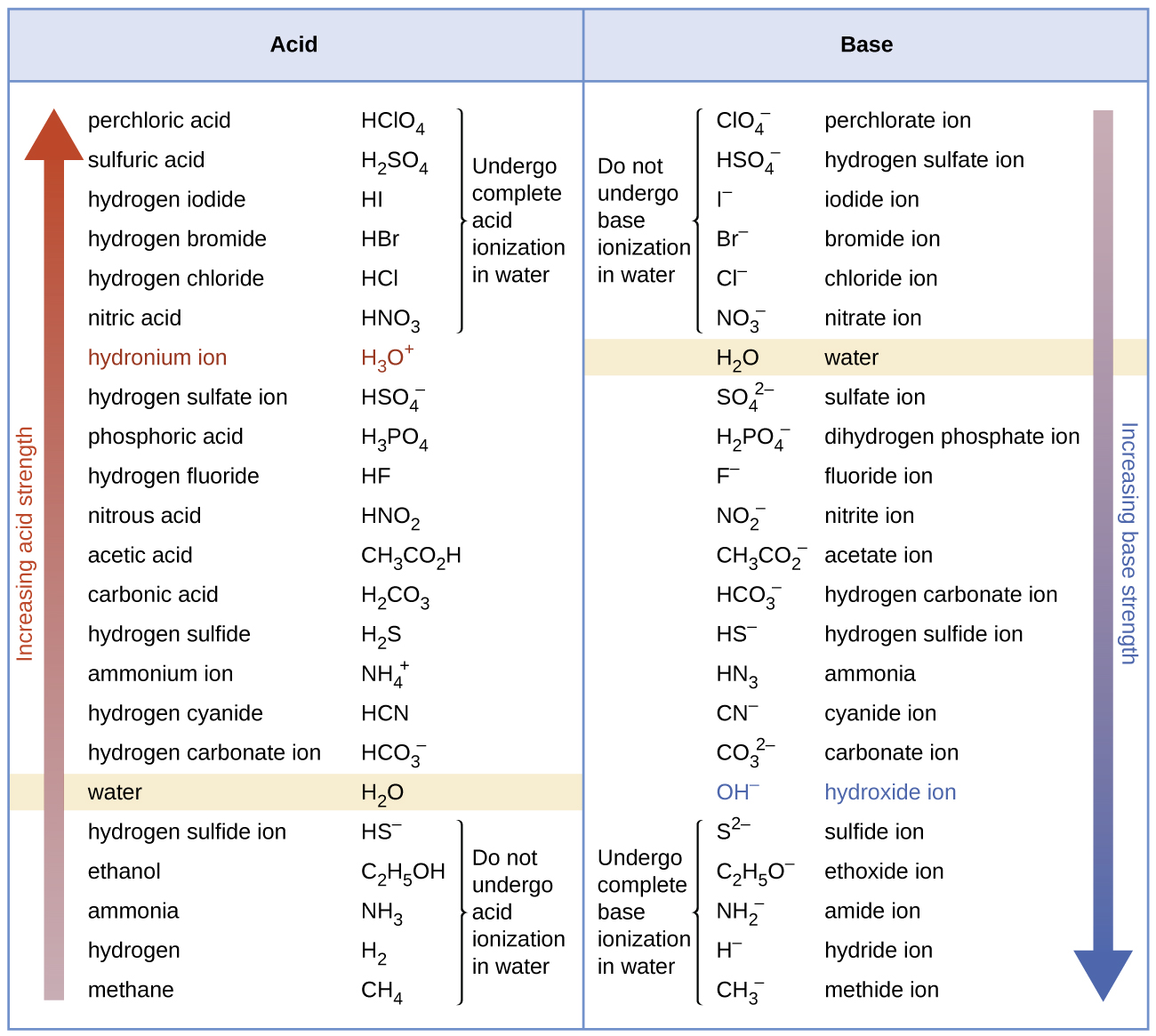
ClO 4 -Perchlorate ion. If the ionization reaction is essentially complete the acid or base is termed strong. Strength- The amount of HOH- ions the acidbase is able to givereceive strength is measured through the ph scale which is from 0-14 Concentration- The amount of.
The relative strength of an acid or base is the extent to which it ionizes when dissolved in water. A concentration acid contains the maximum amount of solutes per unit volume of solution at a given temperature. The Bronsted-Lowry definition of acids and bases defines an acid as a proton donor and a base as a proton acceptor.
Weak acid as compared to the same concentration as strong acid will have. PKb 874. Concentrated ethanoic acid and dilute ethanoic acid are both weak acids because they are only partly ionised in water.
Similarly an acid-base reaction under the Bronsted-Lowry definition entails the transfer of a proton from an acid to a base. And similarly the basic strength of a solution it depends on the concentration of OH minus ions. Titration involves the slow addition of one solution where the concentration is known to a known volume of another solution where the concentration is unknown until the reaction reaches the desired level.
If relatively little ionization occurs the acid or base is weak. Arrange these bases in order of increasing strength. AIn both words and in terms of a mathematical equation describe the relationship between pH and the ratio of conjugate base to acid concentration that you observed in this experiment.
Adding more of the solvent eg water reduces the concentration making the solution more dilute. The strong bases are. The concentration of a solution is a measure of how crowded the solute particles are.
A strong acid or base completely ionizes in a solution while weak acid or base only partially ionizes in a solution. It also applies to how. Acid concentration and strength - Higher A solution forms when a solute dissolves in a solvent.
Up to 256 cash back Include a brief fewer than 4sentence explanation foreach ofthe followingthat cites raw data or information gathered from plots. You can tell the difference between a strong acid and a weak acid. A dilute acid solution is not the same as a weak acid solution and a concentrated acid solution is.
Concentration of Acids is different. The student directions work for both the Java and html5 sims. This is completely different that strength of the solution.
There are many more weak acids and. Note that the strength of an acid is not affected by its concentration. Weaker bases have smaller K b values.
Up to 24 cash back The concentration of an acid or base is the amount of moles per unit volume. Concentrated hydrochloric acid and dilute hydrochloric acid are both strong acids because they are both completely ionised in water. A strong acid does not become a weak acid just because it is diluted.
We will see words like CONCENTRATED and DILUTE. There is a difference between the strength of an acidbase and the concentration of an acidbase. The higher the concentration of H plus ions the more acidic the solution and the lower the concentration of H plus ions the less acidic the solution.
Strong acids and bases are compounds that totally dissociate in solution to create ions. Hydrogen chloride HCl ionizes to produce H and Cl ions upon dissolving in water. Acids are listed in ascending order of strength.
Concentration is the amount of solute something that dissolves that is dissolved in a certain amount of solvent usually water Dissolving more of the substance into a given volume increases the concentration. It refers to how much of an acid the solute is dissolved in the solution.
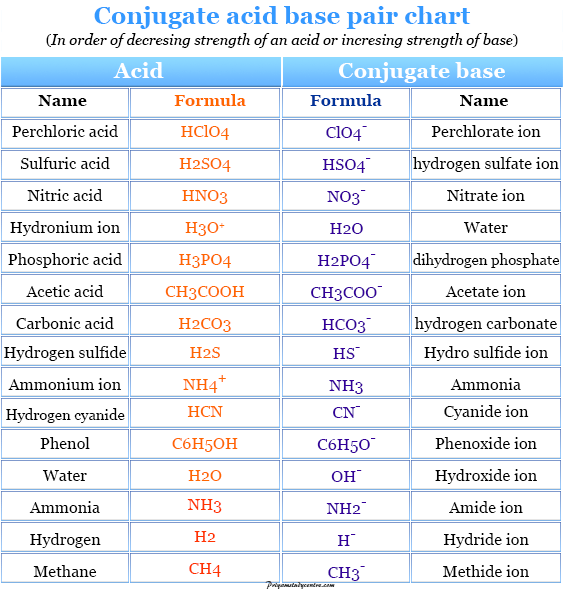
Conjugate Acid Base Pair Definition Concept Examples List

Ph Chart For Acids And Bases Ph Chart Study Chemistry Electron Configuration

Strong Acids And Strong Bases Acids And Bases That Are Strong Electrolytes Completely Ionized Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Education Organic Chemistry Study

Pin On Acids Bases And Solutions
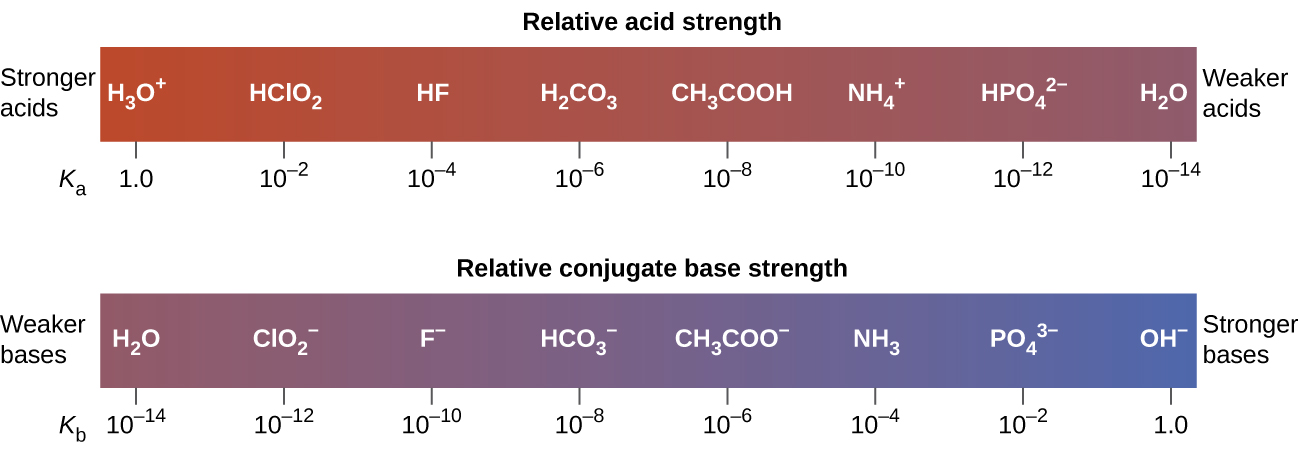
14 3 Relative Strengths Of Acids And Bases Chemistry

Acids And Bases Basic Introduction Chemistry Youtube

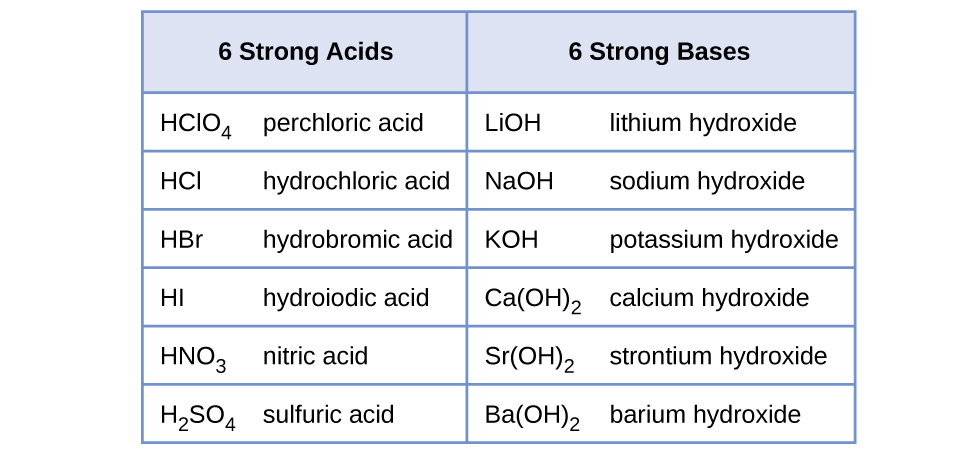
Comments
Post a Comment